Is Stevia Safe? 7 Side Effects That Give You The Answer
As you include it in your diet, know that this sugar-free alternative may not be all good.

Image: Shutterstock
Is stevia good for you? Can you take it regularly? Many of the side effects of stevia might make you wonder about the same. In fact, you may even reconsider using this natural sweetener as many people substitute stevia for sugar to get rid of sugar heartburn and cut calories for weight loss. However, stevia may lead to negative effects. So, if you have been wondering if stevia is safe, this article is for you. Here, we examine the side effects of stevia and its potential medical interactions. Read on to learn more!
In This Article
What Is Stevia?
Stevia is a zero-calorie sweetener which can sometimes taste bitter or have a metallic taste. Several people use it as a substitute for sugar to reduce their calorie intake. It is made of steviol glycosidesi XPowerful, plant-sourced sweeteners with strong antioxidant properties used in small amounts in food and drinks. and is about 200 times sweeter than sugar.
Stevia is derived from a plant. It is part of the Asteraceae family of plants that are native to Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. The prized species of the plant that is used to sweeten food grows in Brazil and Paraguay.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Though its use as a sugar substitute is gaining pace, it is important to note that the FDA does not recognize stevia leaf or its extracts as safe (1).
How Safe Is Stevia?
Is stevia healthy and safe? Well, some believe that stevia may harm the kidneys and the reproductive system if consumed in excess. It may also mutate genes (2). Hence, the FDA doesn’t allow whole-leaf or unrefined stevia in foods. Well, all of this is just one side of the story.
The other side of the story shows later studies stating that stevia is safe in moderate amounts. Though the FDA does not recognize stevia extracts as safe, it has not questioned the use of certain high-purity stevia derivatives in food (1). Hence, stevia products have been available on the market without any major safety concerns. However, this does not necessarily mean that stevia is healthy.
In the following section, we have listed the side effects and health risks of stevia consumption.
What Are The Side Effects Of Stevia?
1. May Cause Gastrointestinal Issues
Some believe that the intake of highly refined stevia may lead to nausea. The steviosides in stevia may irritate your stomach and cause digestive issues, bloating or reduce your appetite.
Studies speculate the role of different artificial sweeteners in promoting gastrointestinal issues, although we need more research to establish the connection (3).
It is also believed that the consumption of stevia may lead to diarrhea trapped gas, and potential gut damage. However, more research is needed in this regard.
Veronika, a blogger, wrote about the side effects she experienced due to using stevia in her blog. She wrote, “However, every day since starting the Truvia (maybe not the first week or so, but after that) I would feel pain, cramping, bloating. For me, it just devastated my system (i).”
2. Could Lead To Hypoglycemia

This is a health benefit that may manifest into a side effect with overuse. Stevia can help lower blood sugar levels (4).
Though there is no direct research, heavy stevia intake (along with blood sugar medications) could lead to hypoglycemia – a condition in which blood sugar levels can become dangerously low.
Hence, we recommend you to stay away from stevia and take your doctor’s advice if you are already on diabetes medications.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?3. May Lead To Endocrine Disruption
There is a possibility that the steviol glycosides can interfere with hormones controlled by the endocrine system. According to a 2016 study, sperm cells, when introduced to steviol, saw an increase in progesterone hormone (secreted by the female reproductive system) (5).
4. May Cause Allergies
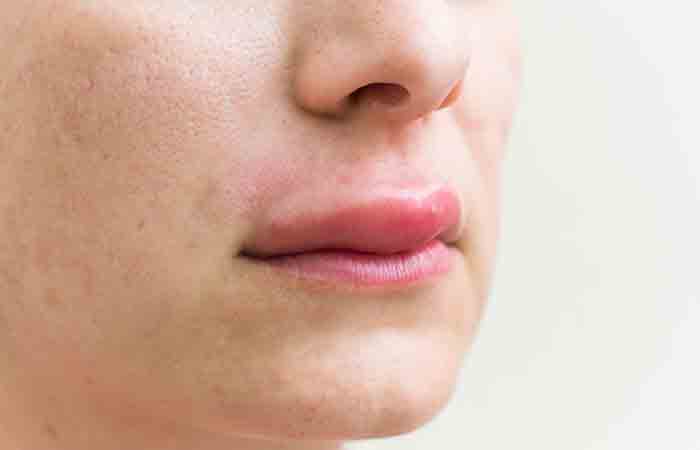
There is no scientific research to support this statement. However, anecdotal evidence suggests that stevia and other artificial sweeteners may cause allergies in some people.
Some believe that there could be allergic reactions if you are allergic to ragweed. The theories state that your body may mistake the proteins in the food you eat as pollen and launch an immune response to react. Symptoms of the allergies may include swelling and itching of the lips, mouth, throat, and tongue, abdominal pain, headaches, dizziness, and vomiting. As there is no research to support this, talk to your doctor before taking stevia (if you happen to be allergic to certain foods).
5. Stevia May Cause Numbness
Though there is very little information on this, some anecdotal evidence refers to individuals experiencing numbness in their hands and feet (and even on the tongue) after taking stevia.
Watch out for these reactions. If you notice these symptoms, stop use and visit your doctor immediately.
6. May Lead To Sore Muscles
There is little research on this aspect. Certain sources state that taking stevia can lead to aching muscles and muscle soreness. In a study, the intake of a drug made of steviosides (the active components of stevia) was found to cause muscle tenderness and pain in certain patients (6).
If you find your muscles are sore for no reason, stop stevia intake and check with your doctor.
7. May Increase The Risk Of Anxiety
Erythritol is a common sugar alcohol found in many stevia products (7). An animal study published in Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry Journal found that erythritol may aggravate gut inflammation. This increased inflammation may lead to anxiety-like behaviors (8). This showed signs of anxiety-like behaviors in the mice group. The study concluded that consuming products with erythritol might indirectly contribute to anxiety by disrupting gut health and causing inflammation.
While the study did not directly mention stevia, it may raise some concerns about the excess use of stevia products containing erythritol. Further research is needed to fully understand its effects on humans.
Who Should Not Use Stevia?
Though research is ongoing, it is believed certain individuals could have a higher risk of contracting side effects with stevia use. They include individuals with:
- Blood pressure issues
- Blood sugar issues
- Kidney conditions
- Heart conditions
- Issues with hormones
Stevia may also cause medical interaction with certain drugs. Individuals who are on medications, especially those aimed at the treatment of the above-mentioned health conditions, are suggested to keep away from stevia.
Does Stevia Interact With Any Drugs?
Stevia may interfere with certain medications. Hence, keep a watch on these combinations.
- Stevia And Lithium
Stevia has diuretic propertiesi XAny drug with properties that increases urine flow and helps the body get rid of extra water, salts, toxins, and waste. . This property may decrease lithium excretion, thereby increasing serum lithium levels, leading to serious issues (9). Hence, if you are already taking some form of lithium, consult your doctor before consuming stevia.
- Stevia And Antidiabetes Drugs
Taking stevia may lower blood sugar levels, and if you are also taking anti-diabetes medication, it may lower your sugar levels way too much. However, more experimental work is required in this area (9). Talk to your doctor before using it. They may change the dose of your diabetes medication. Some of these medications include Amaryl, DiaBetas, Actos, and Avandia.
- Stevia And Antihypertensive Drugsi XDrugs employed to treat high blood pressure and help avoid potential issues like stroke and heart attack.
Some research also shows that stevia may lower blood pressure (9). This is why you need to be careful if you are also taking blood pressure medications. Some of these medications include Cozaar, Diovan, Norvasc, and Lasix.
Stevia has also been associated with cancer. However, research has some interesting findings.
Stevia And Cancer
There is no research stating that stevia may cause cancer. In fact, studies show that stevia may inhibit cancer from spreading. Research suggests that stevia can be a potential chemotherapy agent for cancer treatment (10).
Other studies also state the therapeutic properties of stevia against cancer. This can be attributed to the glycosides they contain (11).
Can pregnant women take stevia? Find out in the next section.
Stevia And Pregnancy
In animal studies, stevia was found to be safe during pregnancy. It did not increase toxicity in rat embryos. It also did not affect the pregnancy or fertility outcomes (12).
However, the safety of stevia during pregnancy and the breastfeeding period in humans is yet to be proven (12). Hence, it is better to avoid stevia during pregnancy.
Infographic: 6 Side Effects Of Stevia
Stevia is a zero-calorie natural sweetener, which is a widely used substitute for sugar to reduce calorie intake. But overuse of stevia can cause a few alterations in several metabolic processes and pathways, which may have severe consequences in the long run. To know about some of stevia’s most harmful side effects, check out the infographic below!

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Stevia is a common sweetener used as a substitute for sugar with zero calories. It is believed that taking this sweetener in moderate amounts is safe. However, the FDA does not recognize the derivatives of stevia as safe while not objecting to the use of high-purity stevia derivatives in foods. The side effects of stevia include gastrointestinal issues, extremely low blood sugar levels, endocrine disruption, sore muscles, and numbness. Moreover, people with certain medical conditions must stay away from this sweetener. And it may also interact with drugs like lithium. So, practice caution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is stevia safe to be used during pregnancy?
There are no human studies to prove that stevia could be safe during pregnancy. We suggest you talk to your doctor before doing so as studies offer mixed opinions.
Can stevia be a part of the keto diet?
Yes, stevia can be a great addition to a keto diet. But remember, moderation is key.
Can stevia harm the kidneys?
Some believe stevia may harm the kidneys as it may have diuretic properties. It may increase the speed at which the body expels water and electrolytes. Since kidneys are responsible for flushing toxins out, it is believed that this may stress them. But there is no research to support this.
Also, since this sweetener has come into the market only recently, its full impact is yet to be determined.
However, a study shows that stevia intake may reduce the risk of kidney damage (13).
Is stevia bad for your teeth?
No. In fact, studies show that stevia can promote dental health as its extracts are considered non-acidogenic (14).
Is stevia better than aspartame?
Stevia seems to be better than aspartame, another sweetener. Some theorize that stevia has beneficial effects on blood glucose when compared with aspartame.
Is stevia inflammatory?
No. On the contrary, stevia exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that help in decreasing inflammation (15).
Can stevia cause heart palpitations?
Stevia extracts can cause a decrease in serum glucose levels, which may lead to tremors and heart palpitations (16).
Is stevia OK for your liver?
Yes. According to a study conducted on rats, stevia leaves help prevent cirrhosis (a late stage of scarring of the liver) (17). However, more human studies are warranted in this regard.
Does stevia raise estrogen?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that long-term intake of stevia may affect estrogen levels. However, limited research is available to prove this claim.
Does stevia cross the blood-brain barrier?
The beta-caryophyllene epoxides in stevia may cross the blood-brain barrier and interfere with the regulation of brain functions. However, more research is needed to prove the same.
Does stevia cause yeast infections?
No. Stevia possesses antifungal properties and can fight against yeast infections (18).
Key Takeaways
- Stevia is a low-calorie sweetener that is native to Paraguay and Mexico.
- A high dose of stevia may decrease fertility and cause kidney issues.
- The stevioside in stevia may irritate your stomach and cause gastrointestinal issues.
- Stevia may interact with antidiabetic medications and lower your blood sugar levels too much.
- While animal studies suggest that stevia is safe for consumption during pregnancy, human studies are warranted to support this claim.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Additional Information about High-Intensity Sweeteners Permitted for Use in Food in the United States. U.S. Food and Drug Administration
https://www.fda.gov/food/food-additives-petitions/additional-information-about-high-intensity-sweeteners-permitted-use-food-united-states#:~:text=FDA’s%20response%20letters%20on%20such,permitted%20for%20use%20as%20sweeteners. - Base substitution mutations in uridinediphosphate-dependent glycosyltransferase 76G1 gene of Stevia rebaudiana causes the low levels of rebaudioside A: mutations in UGT76G1, a key gene of steviol glycosides synthesis, Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24811677 - Artificial Sweeteners: A Systematic Review and Primer for Gastroenterologists, Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4819855/ - Hypoglycemic Effect of Aquatic Extract of Stevia in Pancreas of Diabetic Rats: PPARγ-dependent Regulation or Antioxidant Potential, Avicenna Journal of Medical Biotechnology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4842244/ - In vitro bioassay investigations of the endocrine disrupting potential of steviol glycosides and their metabolite steviol, components of the natural sweetener Stevia, Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0303720716300533 - A double-blind placebo-controlled study of the effectiveness and tolerability of oral stevioside in human hypertension, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2014988/ - Natural sweeteners: the relevance of food naturalness for consumers, food security aspects, sustainability and health impacts
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7504156/ - Erythritol aggravates gut inflammation and anxiety-like behavioral disorders induced by acute dextran sulfate sodium administration in mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37604788/ - Stevia: Medicinal Miracles and Therapeutic Magic, International Journal of Crop Science and Technology.
https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/315800 - Steviol, a natural product inhibits proliferation of the gastrointestinal cancer cells intensively, Oncotarget, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5995179/ - A Review on the Pharmacology and Toxicology of Steviol Glycosides Extracted from Stevia rebaudiana, Current Pharmaceutical Design, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27784241 - Sugar substitutes during pregnancy, Official Publication of the College Family Physicians of Canada, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4229159/ - Steviol Reduces MDCK Cyst Formation and Growth by Inhibiting CFTR Channel Activity and Promoting Proteasome-Mediated CFTR Degradation, PLoS One.
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0058871 - An in vitro and in vivo Comparison of the Effect of Stevia rebaudiana Extracts on Different Caries-Related Variables: A Randomized Controlled Trial Pilot Study, Karger Journals.
https://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/351650 - Effects of stevia on glycemic and lipid profile of type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized controlled trial, Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7103435/ - Effects of Stevia Rebaudiana on Glucose Homeostasis, Blood Pressure and Inflammation: A Critical Review of Past and Current Research Evidence, International journal of clinical research & trials.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7059728/ - Stevia prevents experimental cirrhosis by reducing hepatic myofibroblasts and modulating molecular profibrotic pathways, , US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30338893/ - A SWEET FUTURE FOR STEVIA: A MAGICAL SWEETNER, Researchgate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346306577_A_SWEET_FUTURE_FOR_STEVIA_A_MAGICAL_SWEETNER






























